Triangles and TrigonometryProperties of Triangles
Let’s start simple: a triangle is a closed shape that has three sides (which are
We can classify triangles by the size of their angles:
A right-angled triangle
has one
An obtuse triangle
has one
An acute triangle
has
For convenience, we always label triangles in the same way. The vertices are labelled with capital letters A, B and C, the sides are labelled with lowercase letters a, b and c, and the angles are labelled with Greek letters
The side that lies opposite vertex A is labeled a, and the angle that lies right next to A is labelled
Medians
Here you can see a triangle as well as the
A
It seems like the medians always
Medians always divide each other in the ratio 2:1. For each of the three medians, the distance from the vertex to the centroid is always
The centroid is also the “balancing point” of a triangle. Draw a triangle on some cardboard, cut it out, and find the three medians. If you were accurate, you can now balance the triangle on the tip of a pencil, or hang it perfectly level from a piece of string that’s attached to its centroid:
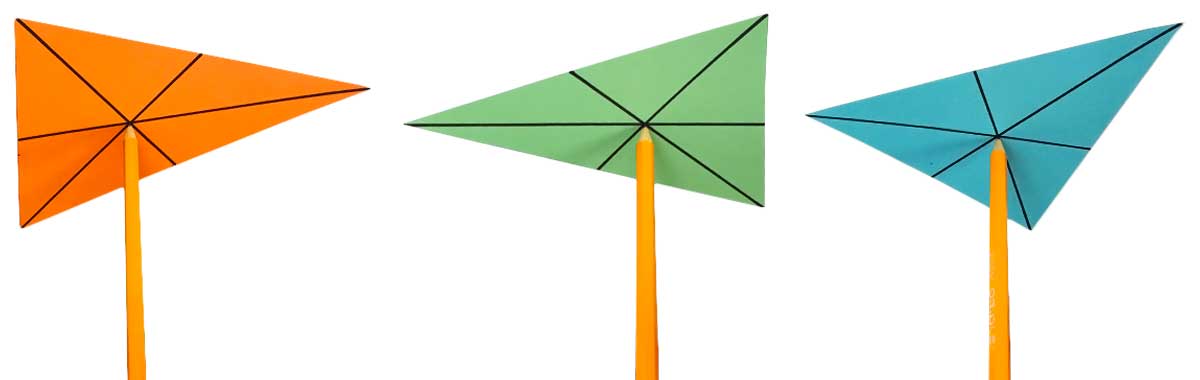
This works because the weight of the triangle is evenly distributed around the centroid. In physics, this point is often called the center of mass.
Perpendicular Bisectors and Circumcircle
Recall that the
Draw the perpendicular bisector of all three sides of this triangle. To draw the perpendicular bisector of a side of the triangle, simply click and drag from one of its endpoints to the other.
Like before, the three perpendicular bisectors meet in a single point. And again, this point has a special property.
Any point on a perpendicular bisector has the same distance from the two endpoints of the lines it bisects. For example, any point on the blue bisector has the same distance from points A and C and any point on the red bisector has the same distance from points
The intersection point lies on all three perpendicular bisectors, so it must have the same distance from all three
This means we can draw a circle around it that perfectly touches all the vertices. This circle is called the
In fact, this means that if you are given any three points, you can use the circumcenter to find a circle that goes through all three of them. (Unless the points are
Angle Bisectors and Incircle
You’re probably getting the hang of this now: we pick a certain construction, do it three times for all sides/angles of the triangles, and then we work out what’s special about their intersection.
Recall that the
Once again, all three lines intersect at one point. You probably expected something like this, but it is important to notice that there is no obvious reason why this should happen – triangles are just very special shapes!
Points that lie on an angle bisector have the same distance from the two lines that form the angle. For example any point on the blue bisector has the same distance from side a and side c, and any point on the red bisector has the same distance from sides
The intersection point lies on all three bisectors. Therefore it must have the same distance from all three
This means we can draw a circle around it, that lies inside the triangle and just touches its three sides. This circle is called the incircle of the triangle, and the center is called the incenter.
Area and Altitudes
Finding the area of a
The width of the rectangle is the length of the bottom side of the triangle (which is called the base). The height of the rectangle is the perpendicular distance from the base to the opposite vertex.
The height divides the triangle into two parts. Notice how the two gaps in the rectangle are exactly as big as the two parts of the triangle. This means that the rectangle is
We can easily work out the area of the rectangle, so the area of the triangle must be half that:
To calculate the area of a triangle, you can pick any of the three sides as base, and then find the corresponding height, which is the line that is
In triangles, these heights are often called
Like the
In
In
In